In this guide
How to quickly test real-world, physical experiences
How to quickly test real-world, physical experiences

Testing customer experiences beyond the screen
Many teams are familiar with testing digital experiences using a human insight solution. But what happens when the customer journey includes real-world elements such as in-store pickup, physical product setup, or using an ATM?
Unfortunately, many companies still rely on outdated methods to gather customer feedback on these physical user experiences. But, leading brands are using human insight solutions to test these real-world experiences as efficiently as digital ones.
This guide explains how experience testing works in real-world contexts and how it helps optimize omnichannel journeys.

Why real-world experience testing matters
Companies can rapidly iterate on digital products—like a pitstop crew in a car race—but physical experiences often move at the pace of a horse-drawn carriage, untested due to cumbersome, expensive traditional market research. This leaves gaps in understanding the full customer experience.
Real-world user testing delivers rapid feedback and enables direct observation of customer behavior during physical interactions. With smartphones and mobile ethnography tools, companies can now:
- Optimize the full omnichannel journey
- Observe real-world product setup and usage
- Analyze customer behavior in natural environments
- Understand what drives customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Uncover latent friction points and unmet needs
This ability to test in real-world environments helps bridge the gap between digital and physical touchpoints, ensuring a cohesive and user-friendly experience throughout the customer journey.
Common real-world experiences you can test
If it can be captured with a smartphone camera, you can test it. Here are several examples of real-world testing scenarios:
- Performing a task: see how users complete a physical task like cooking a recipe or assembling furniture. This helps you understand how your solution fits into everyday routines.
- Unboxing and setup: observe product unboxing to evaluate packaging and first impressions. Assess how intuitive the setup process is and how customers feel about the experience.
- Operating a device: capture how intuitive or confusing it is to use items like smart home gadgets, gaming consoles, VR headsets, IoT devices, or drones. You can even capture footage from the device itself when applicable.
- Using mobile apps in real life: test app usability in noisy, distracting, or changing conditions like shopping, commuting, or selecting a restaurant. Environmental factors such as lighting and motion can impact usability.
- Online-offline journeys: evaluate experiences like ordering online and picking up in store. This is especially relevant for services like curbside pickup, returns, or shipping label creation.
- Shop-alongs: watch how customers navigate stores, interact with signage, find products, and make purchase decisions. See how they compare items and react to packaging or pricing.
- Home walkthroughs: ask users to show and discuss how they use household goods or organize their wardrobes. This reveals preferences and priorities in a personal context.
- Destination-based testing: assess behavior in locations like workplaces, transit, vacation spots, or hotels. This could include evaluating service experiences or filing claims in situ.
- On-the-go experiences: test usability and task completion while walking, riding transit, or moving through public spaces. Anywhere with a wireless signal can be a test location.
ON-DEMAND WEBINAR
Increasing customer satisfaction: turning customer insights into action
Traditional methods fall short
Traditional market research methods for testing physical experiences have several limitations:
- Film crews: expensive, slow to schedule and deploy, and intrusive—often resulting in unnatural behavior
- On-site researchers: less disruptive but still awkward and time-consuming, with limited scalability
- Lab settings: remove the user from their natural environment, missing crucial context and distractions
- Interviews only: rely on memory and self-reporting, which can omit important usability issues or misattribute blame
Due to these limitations, teams often guess or rely on anecdotal internal feedback, like navigating without a map—missing critical insights from real customers that could steer them in the right direction.
Modern solutions for fast real-world feedback
A high-quality human insight solution allows fast, scalable usability studies for physical experiences. Look for tools that offer:
- Access to diverse, opt-in test participants with advanced segmentation capabilities
- Quick test deployment with templates, screeners, and automated targeting
- Smartphone or tablet-based video capture using the backside camera
- AI-powered video feedback, emotion analysis, and summarization tools
- Centralized storage for insights, highlight reels, and stakeholder collaboration
These capabilities allow teams to observe behavior in context, identify friction points, and understand emotional reactions without the delays and cost of traditional research methods.
GUIDE
How to test prototypes that lead to confident, customer-centric design
How UserTesting supports real-world usability studies
UserTesting's platform supports efficient real-world user testing without unnecessary friction. Participants use their smartphones to record product setup, usage, and in-context feedback.
The software is already installed on their devices, making it simple to capture what they see and do. You can ask users to narrate their actions and thoughts, giving you both visual context and direct feedback.
If you need help managing logistics—such as shipping a product to a participant or scheduling visits to specific locations—UserTesting's professional services team can assist with coordination and recruiting.
Tests have been successfully conducted in homes, stores, airplanes, parks, restaurants, hotels, shared homes, and vehicles.
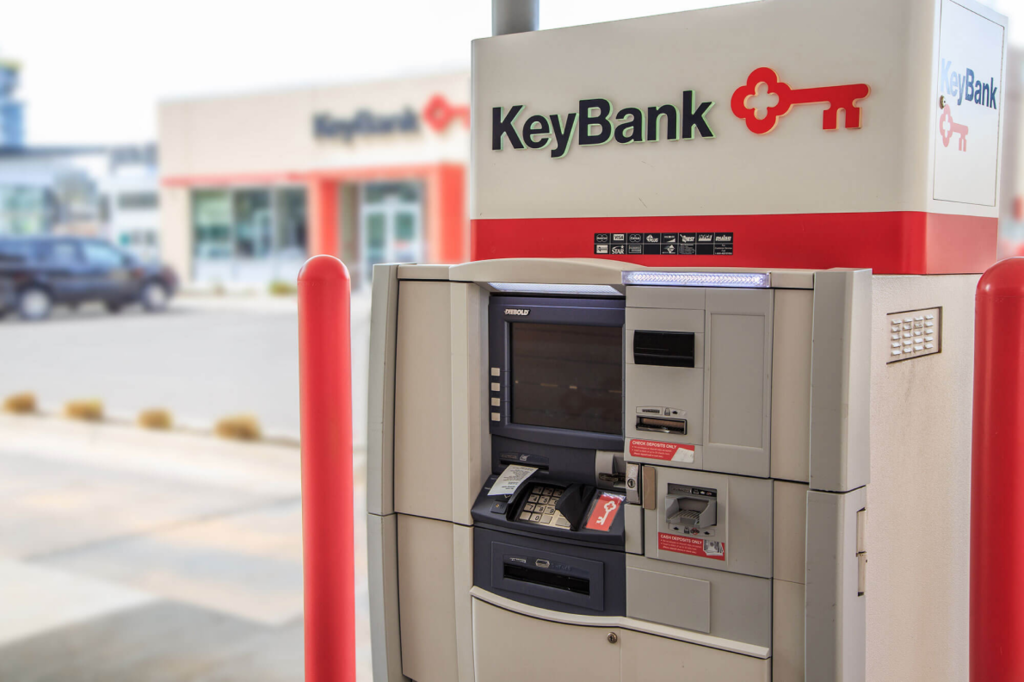

Examples of physical experience testing
- KeyBank: benchmarked ATM usability by sending users to both its own and competitors' kiosks. Insights led to a redesign that reduced confusion and improved overall satisfaction.
- Grooming company: tested an in-store promotion as it expanded from e-commerce to retail. Customers expected to pay for samples that had previously been free online, allowing the company to save millions.
- Shipping company: evaluated the package drop-off experience. Findings revealed customers had difficulty identifying official locations, prompting signage improvements and clearer instructions.
Steps to set up a real-world experience test
- Define objectives
- Step: set clear, actionable goals aligned with business priorities
- Challenge: Aligning stakeholder expectations and ensuring objectives are specific and actionable
- Identify the target audience
- Step: determine relevant customer segments based on demographics or behaviors
- Challenge: avoiding assumptions and ensuring segmentation aligns with the business context
- Select data sources
- Step: choose qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods depending on your needs
- Challenge: ensuring data relevance, completeness, and compliance with privacy regulations
- Collect data
- Step: run moderated or unmoderated tests using smartphone video capture and guided tasks
- Challenge: achieving robust participation, reducing response bias, and handling logistical barriers
- Analyze data
- Step: organize and examine the data to uncover patterns, trends, and behaviors
- Challenge: Dealing with incomplete or conflicting data and avoiding cognitive biases in interpretation
- Synthesize insights
- Step: extract key findings, highlight themes, and build user-centered recommendations
- Challenge: maintaining focus on priorities and ensuring the insights are practical for decision-making
- Validate insights
- Step: confirm the accuracy and relevance of insights through review or supplementary research
- Challenge: identifying blind spots and allocating time and resources for validation
- Communicate insights
- Step: deliver the findings to stakeholders in a format that is clear and actionable
- Challenge: tailoring insights for diverse audiences and ensuring alignment with strategic needs
Additional setup tips for physical usability studies
Determine whether you’ll need help from professional services. Are you looking to have people run the test at home? If so, you can set up the test on your own. If you need them to be at another location, work with the professional services team to recruit people who are willing to go to that location.
Use the screener to make sure people are willing to record the test. Give a brief description of the test you’re looking to do. If you want them to do a particular task or use a common product, be sure they have that product. If you want them to use or unpack a particular product that you send to them in advance, coordinate that with the pro services team.
Choose a smartphone or tablet as the target device for the test. You want people to use the backside camera to record their experience, so be sure they’re using a smartphone or tablet (we recommend smartphone because there are a lot more of them and your test will fill faster).
Set up the test as a web test. This is a little non-intuitive. You’re not necessarily asking them to test anything on the web, but a website test is the most generic user test, so start with that. Have the test point to a blank screen at the start of the test, and give the tester instructions explaining that you want them to record a particular task as opposed to using a website.
Proceed with the test normally. You can give them tasks to perform, questions to answer, and other instructions the same as any other test. Be sure to have them turn on the backside camera when you want to see what they are doing.
Limitations to keep in mind
While real-world testing is flexible, there are a few important limitations:
- Safety: don’t ask participants to record while driving or doing anything unsafe. Instead, simulate scenarios safely.
- Privacy: adhere to privacy laws. Record only in public areas where consent isn’t required, or ensure all parties are aware and agree to recording.
- Connectivity: participants need a stable wireless connection to complete the test. Avoid signal-dead zones or prepare alternatives like store Wi-Fi.
- Two-handed tasks: recommend methods for stabilizing the phone during tasks, such as propping it in a roll of duct tape.
Real-world feedback powers better experiences
Skipping real-world usability studies is like trying to win a race without seeing the track—you're likely to miss essential insights and lose direction in optimizing customer experiences. With the right tools, you can conduct fast, scalable, and ethical tests anywhere your customers go.
Real-world experience testing with human insight solutions helps brands uncover friction, validate solutions, and deliver cohesive, satisfying omnichannel customer experiences.